Supply chains are the backbone of global commerce, but they are often plagued by inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and vulnerabilities to fraud. Blockchain technology offers a transformative solution to these challenges, promising to revolutionize how goods are tracked, managed, and traded. This revolutionary approach leveraging blockchain for supply chain management has the potential to create more secure, efficient, and transparent systems for all stakeholders.
This article explores the profound impact of blockchain on supply chain management, examining how this innovative technology addresses critical issues such as counterfeiting, provenance tracking, and data security. We will delve into the core functionalities of blockchain for supply chains, analyze its benefits for businesses and consumers, and discuss the future implications of this paradigm shift in global trade. Understanding the potential of blockchain technology in creating a more resilient and transparent supply chain is crucial in today’s interconnected world.
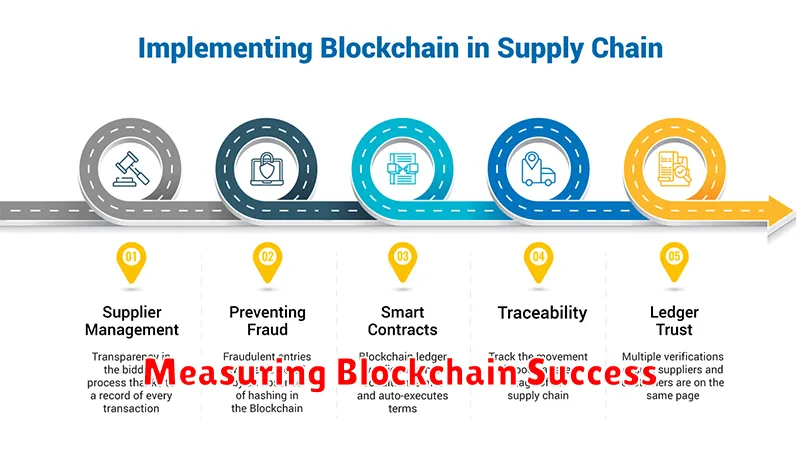
Understanding Blockchain in Supply Chains
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to manage supply chain operations. At its core, a blockchain is a distributed, immutable ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. This eliminates the need for a central authority and creates a single, shared version of the truth.
In a supply chain context, this means every transaction, from the origin of materials to the delivery of the final product, can be tracked and verified. This enhanced visibility empowers businesses to improve efficiency, reduce fraud, and build greater trust with consumers.
Benefits of Blockchain Adoption
Implementing blockchain technology within supply chains offers numerous advantages. Enhanced Transparency is a key benefit, allowing all stakeholders to track products throughout their lifecycle, from origin to consumer. This reduces the risk of fraud and counterfeiting.
Improved Traceability helps pinpoint the source of issues quickly, streamlining product recalls and minimizing disruptions. Increased Efficiency results from automated processes and reduced paperwork. Blockchain’s immutability ensures Enhanced Security, safeguarding sensitive data and building trust among stakeholders.
Cost Reduction is achieved through streamlined processes, minimized reconciliation efforts, and reduced administrative overhead. These combined benefits create a more resilient and efficient supply chain.
Real-Time Tracking and Transparency

Blockchain technology provides unprecedented real-time visibility into every stage of the supply chain. Each transaction, from origin to delivery, is recorded on a distributed, immutable ledger. This allows stakeholders to track the movement of goods with accuracy and efficiency.
This real-time tracking translates directly to enhanced transparency. The shared, secure nature of the blockchain ensures all authorized parties have access to the same information, fostering trust and accountability among participants.
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
Blockchain technology significantly bolsters supply chain security by creating an immutable and transparent ledger of all transactions. This inherent characteristic makes it exceedingly difficult for malicious actors to tamper with data, reducing the risk of fraud.
Each transaction is cryptographically secured and linked to the previous one, forming a chain of custody that is readily auditable. This enhanced traceability allows businesses to quickly identify the origin of counterfeit goods or discrepancies in product information.
By leveraging decentralized consensus mechanisms, blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority, further mitigating the risk of single points of failure and data manipulation. This decentralized structure creates a more secure and resilient supply chain ecosystem.
Reducing Operational Costs
Blockchain technology offers the potential to significantly reduce operational costs across the supply chain. By automating processes and improving efficiency, businesses can streamline operations and minimize overhead.
Reduced paperwork is a key benefit. Digitizing documentation through blockchain eliminates the need for physical paperwork, reducing processing time and associated costs. This also minimizes the risk of errors and fraud.
Streamlined reconciliation is another advantage. Real-time data sharing and immutability facilitate faster and more efficient reconciliation processes. This reduces the time and resources required for auditing and verification.
Implementation Challenges
While blockchain offers significant potential for supply chain transformation, several challenges hinder widespread implementation. Integration with existing legacy systems can be complex and costly, requiring significant modifications to current infrastructure.
Data security and privacy are paramount concerns. Establishing robust access control mechanisms and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations are crucial for successful blockchain deployment.
Furthermore, scalability remains a key hurdle. Blockchain networks must be able to handle the high volume of transactions generated by complex global supply chains efficiently.
Finally, lack of standardization and interoperability across different blockchain platforms pose a significant challenge for seamless data exchange and collaboration among various stakeholders within the supply chain.
Industry Examples and Case Studies
Several industries are actively exploring and implementing blockchain for supply chain management. Food and beverage companies are leveraging blockchain to track products from farm to table, enhancing traceability and reducing food fraud.
Pharmaceutical companies are using blockchain to secure drug supply chains, combatting counterfeit medications and ensuring product authenticity. Luxury goods manufacturers employ blockchain to verify product origins and prevent the sale of counterfeit items, protecting brand integrity and consumer trust.
Specific case studies, such as Walmart’s use of blockchain for food traceability and Maersk’s implementation for shipping logistics, demonstrate the tangible benefits and real-world applicability of this technology.
Future Potential of Blockchain
Blockchain technology holds immense potential to further revolutionize supply chains beyond its current applications. Enhanced automation through smart contracts can streamline processes like customs clearance and payment processing, reducing delays and human error.
Improved data analytics capabilities built upon blockchain’s immutable ledger can provide deeper insights into supply chain operations, enabling more effective demand forecasting and inventory management. This can lead to cost reductions and increased efficiency.
Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate the development of circular economies by enabling better tracking and management of product lifecycles. This can promote sustainability and reduce waste.
Getting Started with Blockchain
Integrating blockchain into your supply chain requires careful planning and execution. Understanding the core concepts of blockchain technology is paramount. This includes distributed ledger technology (DLT), immutability, and consensus mechanisms.
Identify a specific use case within your supply chain where blockchain can provide tangible benefits. This could be improving product traceability, enhancing transparency, streamlining documentation, or combating counterfeiting.
Once a use case is defined, the next step is choosing the right blockchain platform. Consider factors like scalability, security, and cost when making this decision. Then, develop and test a pilot project before full-scale implementation.
Measuring Blockchain Success
Evaluating the effectiveness of a blockchain implementation within a supply chain requires focusing on key performance indicators (KPIs). These KPIs should align with the specific objectives of the blockchain integration.
Cost reduction is a primary driver for many blockchain projects. Track changes in operational costs, such as reduced paperwork, streamlined processes, and minimized discrepancies. Improved traceability is another crucial metric. Measure the time taken to trace products throughout the supply chain and the accuracy of the information obtained.
Enhanced security and reduced fraud are also significant benefits. Monitor security breaches and instances of counterfeit products. Finally, efficiency gains can be measured by analyzing transaction processing speed and overall supply chain velocity.

