In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, edge computing is emerging as a transformative technology, pushing the boundaries of traditional cloud computing. Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, enabling faster processing, reduced latency, and improved bandwidth efficiency. This paradigm shift has profound implications for businesses across diverse industries, unlocking new opportunities for innovation and operational optimization. Understanding the core principles of edge computing, its advantages, and its potential impact is crucial for businesses seeking to leverage its power.
This article explores the fundamentals of edge computing, examining its key characteristics and benefits. We will delve into its real-world applications across various sectors, highlighting the business impact of this disruptive technology. From enhancing operational efficiency and enabling real-time data analysis to unlocking new revenue streams and strengthening security, edge computing is poised to revolutionize the way businesses operate and interact with their customers. By understanding the transformative potential of edge computing, organizations can gain a competitive edge in the increasingly data-driven world.
What is Edge Computing?
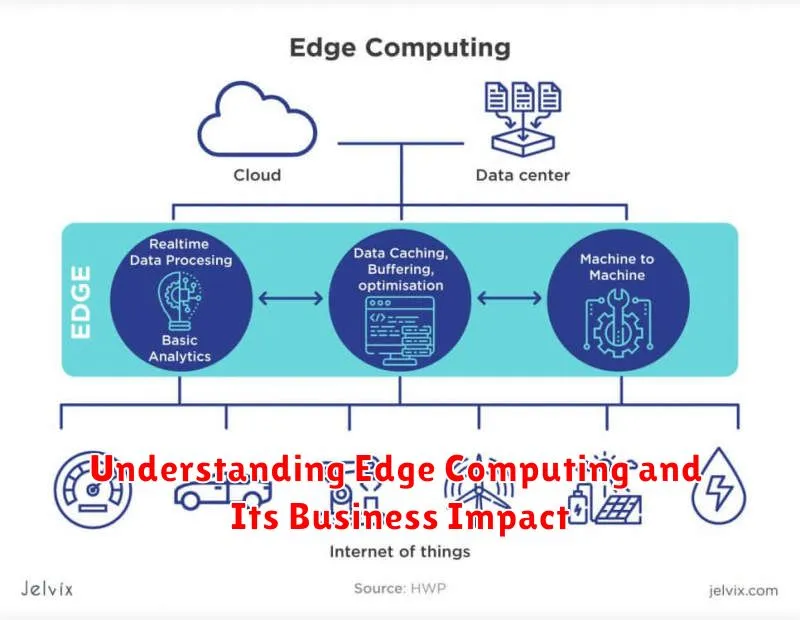
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data. This minimizes latency, reduces bandwidth usage, and enhances data security. Instead of relying solely on centralized cloud servers, edge computing utilizes a network of local edge servers to process data at or near the “edge” of the network, where data is generated.
This approach is especially beneficial for applications requiring real-time processing, such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation. By processing data locally, edge computing enables faster response times and reduces the need to transmit large amounts of data to centralized cloud servers.
Benefits Over Traditional Cloud Solutions
Edge computing offers several key advantages compared to traditional cloud solutions. Reduced latency is a primary benefit, processing data closer to the source drastically minimizes delays. This is crucial for real-time applications like industrial automation and autonomous vehicles.
Bandwidth optimization is another advantage. By processing locally, edge computing reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud, lowering bandwidth requirements and associated costs. This also improves data security, as sensitive information isn’t constantly traversing the network.
Furthermore, edge computing offers improved reliability and resilience. By distributing processing across multiple edge devices, it mitigates the impact of network outages. If the connection to the central cloud is lost, local operations can continue uninterrupted.
Edge Computing for Real-Time Decisions
Edge computing empowers businesses to make real-time decisions by processing data closer to the source. This minimizes latency, which is crucial for time-sensitive applications. Consider a self-driving car needing to react instantaneously to avoid an obstacle. Processing data in the cloud would introduce unacceptable delay.
By analyzing data at the edge, organizations can rapidly respond to changing conditions, optimize operations, and automate processes. This localized processing also reduces the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, saving bandwidth and lowering costs.
Examples of real-time decision making with edge computing include: predictive maintenance in manufacturing, fraud detection in financial transactions, and dynamic pricing in retail.
Security Advantages of Edge Computing
Edge computing offers several key security advantages compared to traditional cloud models. By processing data closer to its source, data in transit is minimized, reducing the risk of interception. This is particularly beneficial for sensitive data subject to strict privacy regulations.
Localized data processing also limits the impact of a potential breach. If one edge location is compromised, the impact is contained, unlike centralized cloud architectures where a breach can jeopardize the entire system.
Additionally, edge computing facilitates faster incident response. Security threats can be identified and addressed more quickly at the edge, minimizing potential damage and downtime.
Applications in IoT and Industry 4.0
Edge computing plays a critical role in the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industry 4.0. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency, bandwidth consumption, and dependence on constant cloud connectivity. This is especially important in industrial settings where real-time insights are crucial.
Key applications include predictive maintenance, where edge devices analyze sensor data to anticipate equipment failures, minimizing downtime. Real-time process optimization is another important use case, allowing for immediate adjustments based on current conditions. Edge computing also facilitates enhanced automation, empowering autonomous robots and other intelligent systems.
Cost Implications for Businesses
Implementing edge computing can involve both upfront and ongoing costs. Initial investments often include purchasing edge hardware, software, and network infrastructure. Businesses must also consider the ongoing operational expenses, such as maintenance, power consumption, and security updates.
While these costs can be significant, edge computing can also lead to cost savings in other areas. By processing data closer to the source, businesses can reduce data transfer costs and latency, leading to improved operational efficiency and potentially reduced cloud storage costs. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is crucial to determine the overall financial impact of adopting edge computing.
Potential Challenges in Adoption
While edge computing offers significant advantages, businesses face several challenges in its adoption. Security concerns are paramount, as distributed edge devices can be vulnerable to cyberattacks. Managing and securing these dispersed devices requires robust security protocols and infrastructure.
Data management presents another hurdle. Effectively handling the vast amounts of data generated at the edge requires efficient data processing, storage, and analysis solutions. Furthermore, integration with existing systems can be complex, requiring significant investment in time and resources.
Skill gaps pose a significant challenge. Finding and retaining skilled professionals with expertise in edge computing can be difficult. Finally, the cost of deploying and maintaining edge infrastructure can be substantial, requiring careful planning and budgeting.
Edge Computing Case Studies
Examining real-world implementations provides a clearer understanding of edge computing’s impact. The following examples highlight diverse applications across various industries:
Manufacturing
Predictive Maintenance: Sensors on machinery collect data, and edge devices analyze it to predict potential failures, minimizing downtime. This allows for proactive maintenance scheduling, optimizing operational efficiency.
Retail
Personalized Shopping Experiences: Edge computing enables real-time analysis of customer behavior, allowing retailers to tailor promotions and offers instantly through in-store displays or mobile apps.
Healthcare
Remote Patient Monitoring: Wearable devices collect patient data, and edge servers process it locally, allowing for timely alerts to healthcare providers and facilitating proactive intervention.
Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure
Integrating edge computing with existing IT infrastructure is a key consideration for successful deployment. A seamless integration minimizes disruption and maximizes the value of both legacy systems and new edge deployments.
This often involves connecting edge devices with existing cloud platforms, data centers, and enterprise applications. Compatibility with current hardware and software is crucial, requiring careful planning and potential upgrades or adaptations.
Furthermore, security must be integrated across the entire system, extending existing security policies and protocols to the edge. This protects sensitive data as it travels between edge devices, on-premises systems, and the cloud.
Future Trends and Predictions
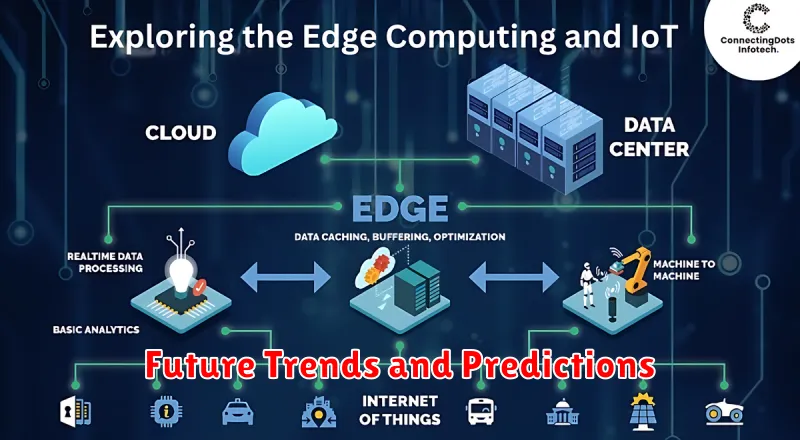
Edge computing is poised for significant growth. Increased demand for low-latency applications, coupled with the expansion of 5G and IoT devices, will drive further adoption.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will become increasingly integrated with edge computing, enabling more sophisticated data processing and analysis at the edge. This will unlock new possibilities for real-time decision making and autonomous systems.
Security remains a critical concern. Expect to see advancements in secure edge computing architectures and technologies to address evolving threats.